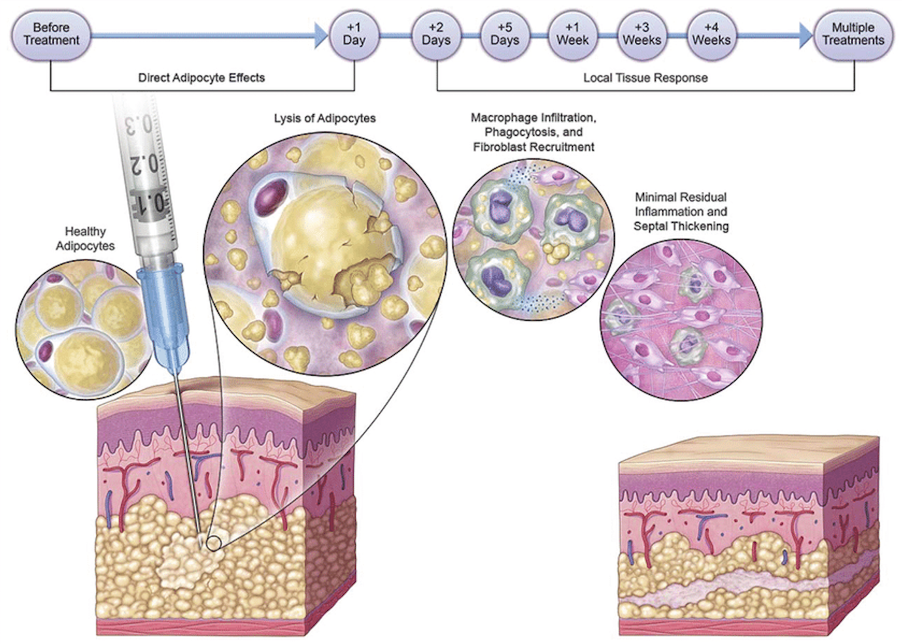
How do
FAT DISSOLVING INJECTIONS WORK?
Deoxycholic acid injection is a cytolytic drug indicated for improvement in the appearance of moderate to severe fullness associated with submental (neck) fat, also called “double chin,” in adults. Deoxycholic acid is a bile acid naturally produced by our livers.
The safe and effective use of Deoxycholic acid for treatment of subcutaneous fat outside of the submental region has not been established. Deoxycholic acid is injected into the fat under the chin and other areas. Multiple treatments are required and will be given at least 1 month apart.
Fat Dissolving treatment can be performed on its own or combined with other procedures for complete facial rejuvenation, such as:
Fat Dissolving Injections Treatment Areas

RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS
The possible side effects include without limitation:
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Pain
- Numbness
- Redness
- Areas of hardness
- Tingling
- Itching
- Nodules
- Skin tightness
- Headache
Tailored Results
Frequently Asked Questions
● Do NOT take anti-inflammatory/blood thinning medications, such as Aspirin, Vitamin E, Fish Oil, Ibuprofen, Motrin, Advil, Aleve and other NSAIDS (can increase the risk of bruising and swelling after injections).
● Do NOT receive skin or laser treatment after injections for at least 10 days.
● Do NOT consuming alcohol or salts to avoid excess swelling.
● Do NOT perform activities involving straining, heavy lifting, or vigorous exercise for 24 hours
● Do NOT receive skin or laser treatment after injections for at least 10 days.
● Apply ice frequently (5-10 minutes every 30 minutes) for up to 6 hours.
● Apply Arnica pilules or Hirudoid cream (available from local pharmacy) may be help to reduce bruising.
● Review after 2 weeks of your treatment.
● LED Light Therapy may be used to help reduce swelling and bruising
● Active infection at the treatment site
● A neurological disorder
● Pregnancy or breastfeeding
● Lidocaine sensitivity
● History of keloid scarring
● Previous use of permanent fillers in the treatment area
● Autoimmune disease
● Porphyria (enzyme disorder)
● Bleeding disorders